Radiation exposure has been a great concern over recent years. For this reason, there are various shielding materials to block radiation and protect individuals from the harmful effects of exposure.
Ionizing radiation is widely used in the medical departments and industries and can cause microscopic damage to the living tissue.
High exposure levels of ionizing radiation cause tissue damage while low exposure levels increase the risk of cancer.
Radiation blocking materials reduce radiation exposure using a simple protective principle of time, distance, and shielding material.
But what are the best materials to block radiation? Let’s learn more about radiation shielding materials.
Materials for Shielding Against Ionizing Radiation
Radiation shielding is of great concern in medical x-ray rooms, nuclear power facilities, particle acceleration processes, and in other circumstances. The shielding materials help reduce exposure to radiation and protect employees from harmful effects of radiation as they operate radiation-emitting equipment.
Before considering the shielding material, you have to identify the type of radiation you want to shield against. The 3 major types of radiation you should worry about include:
- Alpha and Beta particles: Alpha particles consist of helium nuclei which are positively charged and are easy to block, while Beta particles are very difficult to shield since they consist of negatively charged electrons.
- X-rays and Gamma rays: The electromagnetic radiation emitted by these two types of radiation has higher energy levels than that from ultraviolet rays and visible light.
- Neutron particles: These particles do not have any positive or negative charge. They generate high energy levels that need to be blocked.
Indirect ionizing radiation in forms such as gamma rays, x-rays, and neutrons have a different degree of regulating radiation penetration, while direct ionizing radiation involves charged particles.
The best anti-radiation material depends on the type of radiation you want to shield yourself from. Different shielding materials can work better on specific types of radiation than on others.
If you want to shield yourself from ionizing radiation, then materials that have high hydrogen content are great for your protection. If you’re protecting yourself from less ionizing radiation, then material made of lead can do a perfect job.
Lead has been widely used for radiation shielding because of its heavy atomic weight. However, lead material cannot shield you from high-level ionizing radiation such as radiation from meltdowns. When heavy ionizing radiation hits the lead material made of heavy atoms, it results in more ionizing radiation.
How Shielding Products Reduce Radioactive Particles Energy
Radiation shielding products use the principle of attenuation to block radiation from penetrating the material. Attenuation is the gradual loss of intensity when a particular substance flows through a barrier. It reduces the radiation waves by either blocking them or bouncing the particles after hitting the barrier material.
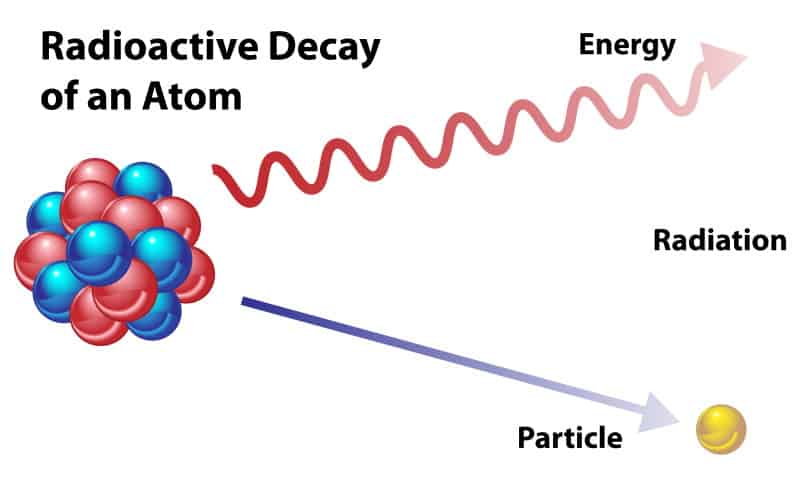
Radiation shielding materials attenuate harmful particles with the ability to interact with your cellular material and destroy healthy DNA.
For example:
- The shielding materials act as a barrier that de-energizes the charged particles that contain electrons. As the charged particles pass through the barrier, they lose electrons and they are no longer a threat.
- Both elastic and inelastic scattering combination helps reduce the harmful effects of neutrons.
- Radiation from x-rays and gamma rays are attenuated through photoemission, scattering processes, and pair production. The photoemission process exposes metals to light in order to produce electrons, while the scattering process uses certain material that scatters the particles to reduce their concentration and trajectory.
Depending on the type of exposure you experience, you can choose a shielding material based on:
- shielding effectiveness;
- strength of the material;
- financial efficiency of the product;
- resistance to environmental damage;
- thermal properties; and
- density and thickness of the material.
The basic radiation protection safety tips involve the use of time, distance, and shielding.
How long you spend in a radioactive environment determines your exposure levels. Therefore, you should limit your exposure to a minimal amount.
You should also stay as far as possible away from the radiation-emitting device. The intensity of radiation is reduced with distance. The farther you move from the radiation source, the less the exposure you have.
Using an effective shielding material is another great approach to reducing your exposure to the harmful effects of radiation.
So What Are The Best Shielding Materials?
The best protection materials that shield against radiation include lead, concrete, and water. You can also use a combination of these shielding materials to protect yourself against ionizing radiation.
Each of the above shielding materials has its own benefits and features. Depending on the type of radiation you want to shield against, you have to consider the above factors before making your decision.
For years, lead has been the leading component in the manufacture of radiation shielding products such as protective garments. Due to the limitations of lead, there are more shielding materials in the market now.
You can choose the best shielding products depending on the type and amount of radiation exposure. There are two types of radiation: direct ionizing radiation and indirect ionizing radiation.
They work by removing an electron in the uncharged particles of indirect ionizing radiation such as x-rays, gamma rays, and neutrons to create free radicals, or use shielding material that blocks charged particles of direct ionizing radiation such as electrons and alpha rays. The shielding material properties directly affect the atoms or molecules in an electron.
Therefore, each shielding product can block specific particles or elements hence the need to have different shielding materials to block different types of radiation.
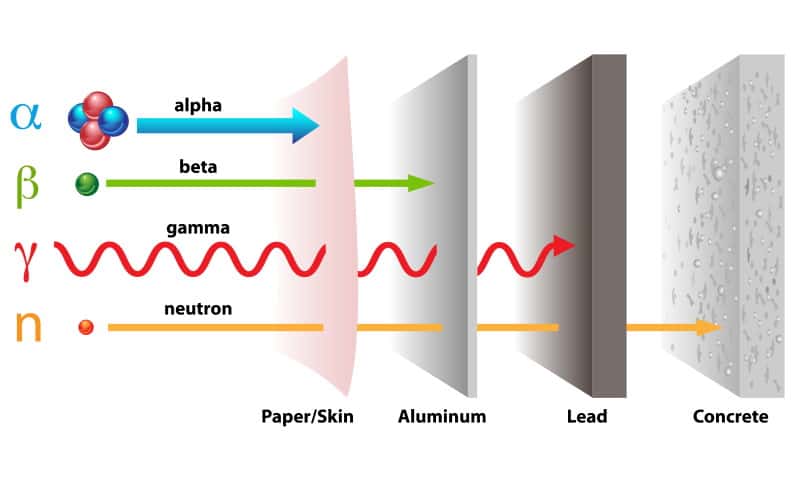
Shielding Materials for X-rays and Gamma Radiation
The density and thickness of radiation blocking material determines its effectiveness. High-density shielding materials are more effective than low-density shielding materials in reducing radiation intensity.
However, you can use low-density materials with increased thickness to increase the effectiveness of blocking radiation.
Shielding material made from lead has a high atomic number and reduces the effects of radiation from gamma and x-rays. The atomic number represents the number of protons present in an atom. Thus, the lead atom consists of a high number of protons as well as a corresponding number of electrons.
The electrons act as a barrier by blocking the x-rays and gamma particles trying to penetrate through the lead material. The thicker the shielding barrier, the higher the degree of protection.
Although you can adjust the thickness of the material to increase the amount of protection, small amounts of radiation may pass through.
If you’re working in industries with high levels of radiation from x-ray equipment, some rays can penetrate through the lead shielding fabric. In this case, lead shield material will not give you an absolute barrier.
Lead material is used to create different forms of products that shield you against radiation. The different products designed include: lead sheets, foils, bricks, pipes, glass, lead-clad tubing, etc.
For example, lead material can create radiation shielding garments such as lead aprons and blankets used by patients and workers during medical x-rays. The attenuation qualities of lead make it the most preferred shielding material to protect against radiation.
Lead material is also blended with other lightweight metals or heavyweight metals to form a lead composite shielding. For example, you can make a composite shielding garment from a blend of lead, rubber, tin, PVC vinyl, etc.
Alpha and Beta Shielding Materials
The density of the shielding material remains an important factor when choosing the best shield for alpha and beta particles. In this case, the thickness of the material is not of much consideration because a single centimeter of plastic or half-inch of paper is enough to shield against alpha particles.
Since lead is not suitable for blocking particles with high atomic number and density, instead use a plastic shield. In certain circumstances, lead cannot block beta particles because they generate secondary radiation as they pass through elements that have high density and atomic number.
When the plastic shield is used, it forms an efficient barrier to block radiation from high-energy beta particles.
For example, you can use tungsten which is a high-density material to block electrons from negatively charged beta particles. The negatively charged particles can also make the tungsten barrier irradiated. In addition, the high-energy beta particles can move two or more meters in the air.
Neutron Shielding Materials
Again, a lead shield can’t block neutron radiation because neutrons don’t have any charged particles and can pass through any dense material. Therefore, any shielding material with a low-atomic number of elements can shield against neutron radiation.
The material forms a cross-section that highly interacts with neutrons blocking radiation emitted. Hydrogen based material or any hydrogen atoms compound with a high concentration such as water can block neutron radiation. The use of hydrogen compounds to create a neutron barrier is inexpensive.
However, the low-density material not only blocks neutrons but also emits gamma rays. So for effective shielding of neutron radiation, you need to combine materials with a high and low-atomic number of elements to create a neutron barrier.
The low-density shielding material will use an elastic scattering process to disperse neutrons, while high-density shielding will use inelastic scattering to block gamma rays.
This combination of elements provides you with effective protection against neutron radiation.
How To Measure Radiation Exposure
If you work in a high radiation environment, you have to measure your radiation exposure in order for you to decide what shielding material you need.
You need to wear a dosimeter if you work in an environment with a high amount of radiation. A dosimeter records the amount of radiation you’re exposed to as you go on with your duties.
If the radiation data recorded per week exceeds 400 microsieverts, then you need to increase your protection. More steps should be taken to maximize the protection of the facility.
Conclusion
There are different shielding materials you can use to protect yourself against radiation. The choice of material to use depends on the type of radiation you want to block. Each of the different types of shielding material has its own properties and benefits.
You also have to consider several factors before making your decision on which shielding material to use. Whether you’re experiencing direct or indirect ionizing radiation, you can choose a shielding product that blocks a particular particle or element effectively.